How Epididymis and Vas Deferens Function Together in Sperm Transport and Fertility
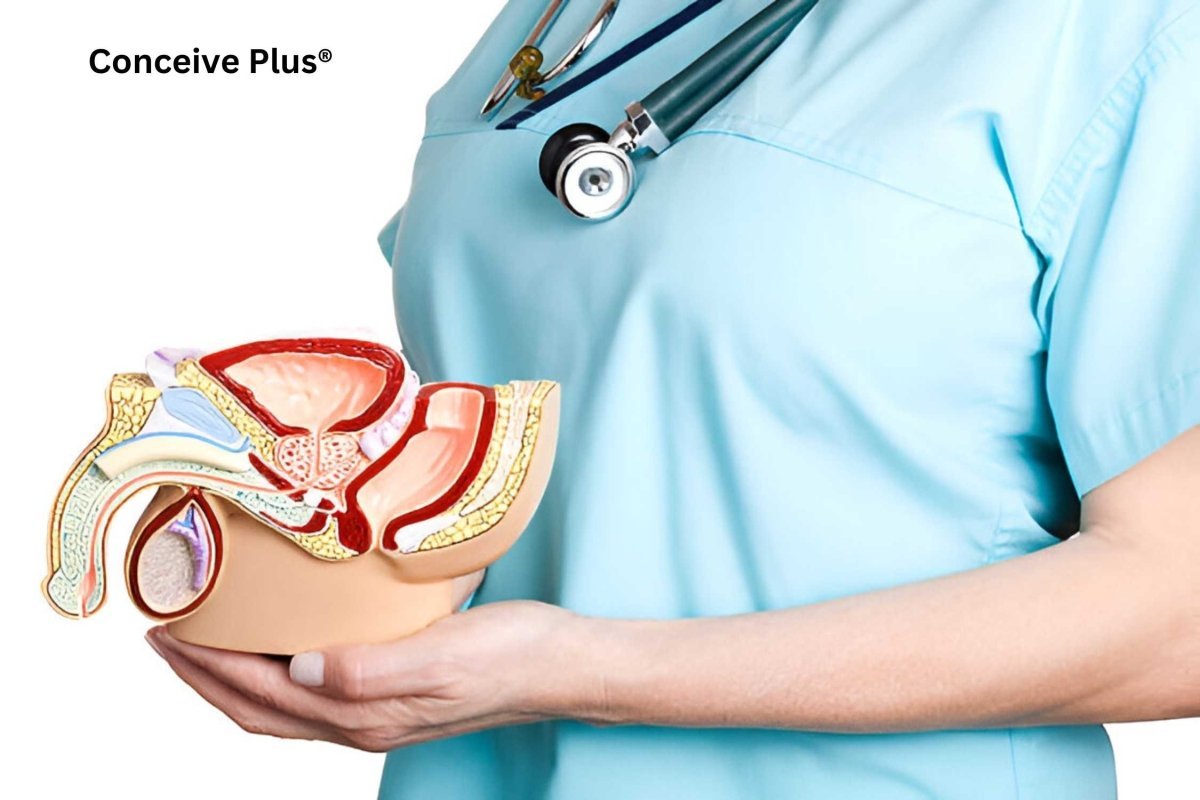
Alright, let's talk about the epididymis and vas deferens. These two are like a tag team in the male reproductive system. Both are super important for transporting sperm and, honestly, without them, male fertility would be a no-go. It's one of those things that’s happening behind the scenes, but we rarely think about it.
What is epididymis and how does it work?
So, first off, what is epididymis? It’s a long coiled tube on the back of the testicle. Think of it like a training camp for sperm. The epididymis function is basically to store and mature sperm. They arrive there, fresh from the testes, but they’re not ready for action yet. They need time to develop. And that’s what is the function of the epididymis. It’s all about making those sperm ready for the big game. Without the function of epididymis, sperm wouldn’t have the energy or the ability to swim properly. No swimming means no fertilization [1].
But you might ask, what is function of epididymis? Well, it’s the final touch in sperm development. Sperm matures in this structure, gaining the strength it needs to fertilize an egg. So yeah, the function of the epididymis is crucial for fertility [2].

Where is the epididymis?
People often wonder, where is the epididymis? It’s right behind the testicles, neatly tucked away. The best way to visualize it is by looking at an epididymis diagram. The sperm spends some quality time there before it's ready for action, maturing over a period of days.
Once sperm is mature, they move from the epididymis into the vas deferens. It’s almost like a relay race, where one team member (the epididymis) hands the baton (sperm) to the next (the vas deferens) [3].
What is the vas deferens and what does it do?
The vas deferens is the next stop. It’s a long tube, often referred to as the sperm tube, responsible for moving sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. But really, what is the purpose of the vas deferens? Well, it’s the sperm highway. The vas deferens function is to ensure sperm gets where it needs to go during ejaculation [4].
The function of vas deferens is just as important as the work done by the epididymis. It’s the bridge, the transporter. Think of it like a delivery service, making sure the sperm reaches its destination. The function of the vas deferens ensures that sperm is released during ejaculation and mixed with seminal fluids [5].
Curious about what is a vas deferens? It’s that same tube running from the epididymis to the urethra, and it’s absolutely essential for sperm transport. A vas deferens diagram can help you see exactly where it runs, tucked inside the body, doing its job behind the scenes [6].
How epididymis and vas deferens work together
The epididymis and vas deferens are like partners. One stores and matures the sperm, and the other transports it for ejaculation. Without one, the other can’t function properly. The function of the epididymis is to ensure that sperm matures and gains the ability to swim. Meanwhile, the vas deferens connects to the urethra, where sperm mixes with seminal fluid. So, during epididymis ejaculation, the epididymis vas deferens work together to make sure sperm is ready to be released [7].
And the key question: what is the function of the vas deferens? It’s simply to make sure that sperm is delivered, without any interruptions, to the urethra, where it can exit the body. The whole system relies on this smooth function, and any blockages or damage to the vas defrens could mean trouble [8].

What happens when there's damage?
If there’s any damage to the epididymis or vas deferens, it can lead to serious fertility issues. Inflammation, like epididymitis, can cause swelling in the epididymis, which blocks the flow of sperm. Similarly, blockages in the vas defrens or vas deference can prevent sperm from reaching the urethra, affecting ejaculation and, ultimately, conception [9].
Doctors usually diagnose such issues by looking at a diagram of epididymis or a diagram of vas deferens. This can help them identify any potential blockages or structural issues that are stopping sperm from traveling smoothly through the vas deferens. They also examine the parts of a scrotum, which include the testicles, epididymis, and vas deferens, to check for any abnormalities [10].
Which tubes carry sperm directly to the epididymis?
Before sperm reaches the epididymis, it has to travel through tiny ducts. So, which tubes carry sperm directly to the epididymis? These are the efferent ducts, which move sperm from the testicles to the epididymis for storage and maturation. It’s here that the sperm matures and gets ready to move to the next step: the vas deferens [11].
The Bottom Line
In short, the epididymis and vas deferens are essential parts of male fertility. Maintaining cool testicles has been shown to support optimal sperm production and overall testicular health. They work together to ensure that sperm matures and is transported properly during ejaculation. The function of the epididymis is all about maturing the sperm, while the function of the vas deferens ensures sperm is transported to the urethra. Keeping these structures healthy is essential for anyone trying to conceive [12]. Male fertility supplements with ingredients like Zinc, Folate, and L-Carnitine may help support sperm quality and reproductive health.
FAQs
What is the function of the vas deferens?
The function of the vas deferens is to transport mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
What is the function of epididymis?
The function of the epididymis is critical to ensure sperm matures properly. Once matured, it is transported through the vas deferens, ensuring that sperm is ejaculated successfully. So, what is the function of epididymis? Simply put, it ensures that sperm is ready for fertilization by the time it leaves the body.
Which tubes carry sperm directly to the epididymis?
The efferent ducts carry sperm directly to the epididymis from the testicles.
Can blockages in the vas deferens cause infertility?
Yes, blockages in the vas defrens or vas deference can prevent sperm from reaching the urethra, causing fertility issues.
What is the purpose of the vas deferens?
The purpose of the vas deferens is to transport sperm from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation.
Citations
- ames ER, Carrell DT, Aston KI, Jenkins TG, Yeste M, Salas-Huetos A. The Role of the Epididymis and the Contribution of Epididymosomes to Mammalian Reproduction. Int J Mol Sci. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7432785/
- Cornwall GA. New insights into epididymal biology and function. Hum Reprod Update. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2639084/
- Turner TT, Lysiak JJ. Oxidative stress: a common factor in testicular dysfunction. J Androl. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18567643/
- Jenkins TG, Carrell DT. The sperm epigenome and potential implications for the developing embryo. Reproduction. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22495887/
- Gage MJ. Complex sperm evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3311381/
- Cooper TG. The epididymis, cytoplasmic droplets and male fertility. Asian J Androl. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3739406/
- James ER, Carrell DT, Aston KI, Jenkins TG, Yeste M, Salas-Huetos A. The Role of the Epididymis and the Contribution of Epididymosomes to Mammalian Reproduction. Int J Mol Sci. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7432785/
- Sullivan R, Frenette G, Girouard J. Epididymosomes are involved in the acquisition of new sperm proteins during epididymal transit. Asian J Androl. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17589785/
- Cornwall GA. New insights into epididymal biology and function. Hum Reprod Update. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2639084/
- Cornwall GA. New insights into epididymal biology and function. Hum Reprod Update. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19136456/
- Holstein AF, Schulze W, Davidoff M. Understanding spermatogenesis is a prerequisite for treatment. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC293421/
- Orgebin-Crist MC. Sperm maturation in rabbit epididymis. Nature. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6074957/













