Sperm Videos: How Are They Important For Reproductive Health
Sperm cells are as small as any other single cell in your body. You can't see sperm with the naked eye. You can't observe the movement of sperm and the union of sperm and egg with the naked eye.
However, with technological advancement, sperm video, sperm movement and the fertilization process can be seen in detail [1].
In the microscopic videos, sperm appear as tiny cells with a head and a tail. You can spot the movement of the sperm tail that pushes the sperm forward. Watching sperm under a microscope provides a compelling look into male reproduction.
How Sperm Appears Under Microscope?
Under a microscope, sperm cells look like tiny tadpoles. Sperm has a round head, which contains the genetic material. Behind the head is a midsection packed with energy to fuel sperm movement.

The moving structure in microscopic videos of sperm is the tail. The long tail moves in a whip-like pattern and helps the sperm move forward [2]. Their fast, organized, and purposeful movement is the most interesting part of watching sperm videos.
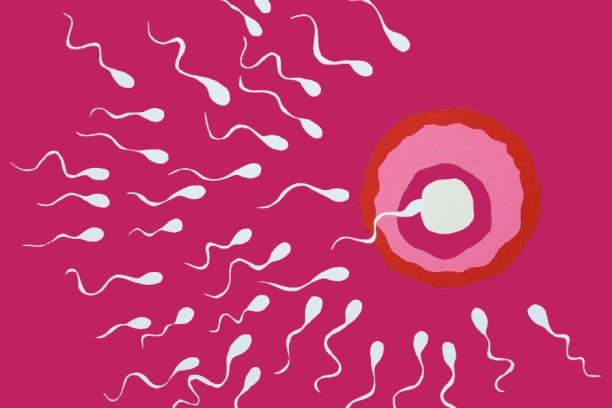
Journey of The Sperm
The journey of sperm begins in the male reproductive system. Millions of sperm are released during ejaculation, but only a few make it to the egg [3].
These videos showcase the incredible journey of sperm as they navigate the female reproductive system. The movement of sperm is driven by their flagella, a whip-like tail that propels them forward.
Here are some key steps in the sperm journey:
-
Sperm Motility
After intercourse, man sperm cells begin their journey through the female reproductive system. They swim from the cervix and uterus to reach the fallopian tubes.
Sperm move in a rhythmic, wave-like motion, using their energy to travel toward the egg. Out of millions, only a few sperm will reach the egg, making sperm motility critical to successful fertilization.
-
Sperm-Egg Interaction
When sperm reach the egg, the race isn’t over. The sperm must penetrate the egg’s outer layer using special enzymes stored in their head [4]. Once a sperm enters the egg, its genetic material fuses with the genetic material in the egg. This interaction begins the process of fertilization and the creation of a new life.
-
Fusion of Sperm and Egg
After the sperm enters the egg, the two cells combine their DNA to form a zygote, the first step in developing a new embryo. Only one sperm can successfully fertilize the egg, and once it does, the egg blocks other sperm from entering. This fusion is the first step of a potential pregnancy.
Importance of Sperm Videos
Sperm videos and information about the working mechanism of sperm cells can be important for the following reasons:
- Educational Importance: Sperm videos are very valuable tool for teaching and learning about male reproductive health. It allows students to visualize and study how sperm swim and their role in fertilization.
- Diagnostic Importance: Watching sperm in real-time helps doctors assess sperm quality, motility, and shape. This leads to better diagnoses of fertility issues in men.
- Development of Technology: Sperm videos contribute to the advancement of male infertility treatment and reproductive technologies. Information about sperm movement improves tools like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) [5].
The Bottom Line
Videos of sperm are really great tools for understanding the complex science behind sperm's workings. They show viewers the interesting interaction of sperm and egg and provide insight into the process of fertilization.
Microscopic videos of sperm moving or fertilization are very valuable for helping people understand the beginnings of life.
Have you ever watched a video of sperm before coming to this article? What did you find most interesting in those microscopic videos? Write your thoughts and perspective in the comments.
Resources Used
- Daloglu, M. U., & Ozcan, A. (2017). Computational imaging of sperm locomotion. Biology of Reproduction, 97(2), 182-188. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/iox086
- Gadêlha, H., Hernández-Herrera, P., Montoya, F., Darszon, A., & Corkidi, G. (2020). Human sperm uses asymmetric and anisotropic flagellar controls to regulate swimming symmetry and cell steering. Science Advances. https://doi.org/aba5168
- What is Sperm? (2023, December 22). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/sperm-and-semen-faq
- Khawar, M. B., Gao, H., & Li, W. (2019). Mechanism of Acrosome Biogenesis in Mammals. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 7, 470641. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00195
- Eskew, A. M., & Jungheim, E. S. (2017). A History of Developments to Improve in vitro Fertilization. Missouri Medicine, 114(3), 156-159. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6140213/













